Round Robin is a balancing mechanism used by the DNS servers which are usually used for sharing the network load and managing the load of geographically distributed Web servers. The DNS server that uses the round-robin mechanism will provide alternates for each client request.
Concept:-
Suppose, you have a domain name and three identical home pages hosted on three servers with three different IP addresses. By using Round Robin DNS, when one user accesses the home page, the request will be sent to the first IP address. The second user who accesses the home page will be sent to the next IP address, and the third user will be sent to the third IP address.
In each case, once the IP address is used out or taken, then that particular IP address will go to the end of the list. Therefore, the fourth user will be sent to the first IP address, and so on. Thus, we can distribute the load across several servers with identical configuration.
The IP addresses in the return list will be in a cyclic or round-robin order which is controlled by the RR-set order of DNS. The IP address which is taken from the list will be used for a specific session and not for each request. ie, The round-robin load balancing mechanism is not likely to distribute the load on a per-request basis and it is most likely to be on a per-session basis.
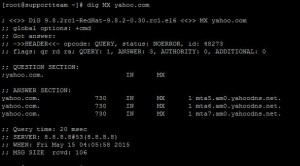
Example for round-robin DNS:-
If a domain name has multiple IP addresses or a domain using multiple MX records with the same priority.
Working:-
>> Setup servers with individual IP addresses and place identical web files on each server.
>> Create A records for a domain in the DNS server to each IP addresses with a lower TTL value.
yahoo.com. 1301 IN A 206.190.36.45
yahoo.com. 1301 IN A 98.138.253.109
yahoo.com. 1301 IN A 98.139.183.24
>> Define RR-set order (cyclic – round-robin) in the DNS configuration file (/etc/named.conf).
Then the DNS server such as BIND will rotate the IP addresses and give it to the remote clients.
/etc/named.conf
=============
options {
rrset-order {
order cyclic;
};
};
rrset-order supports three different orders :-
fixed : Return matching records in the same order
random : Return matching records in random order
cyclic : Return matching records in cyclic (round robin) order
eg:-
options {
rrset-order {
class IN type ANY name “*” order cyclic;
};
};
By default, DNS uses round-robin mechanism to rotate the order of RR (Resource Record) data, when multiple RR’s of the same type exists for a queried domain name.
If round robin is disabled for a DNS server, then the order of the response for the DNS queries will be based on a static ordering of RR which is same as they are stored in the DNS zone file. This is the default behavior of most DNS servers.
The effects of DNS caching will destroy the effectiveness of round-robin DNS unless the TTL value is set to zero. However, when we set the TTL value is zero, then every time a request should be made to the DNS server which will, in turn, increases the server load. So, the preferable TTL value is set to 10 to 15 minutes for availing the benefits of both caching and round-robin DNS in the load balancing mechanism.
If you require help, contact SupportPRO Server Admin