Logstash (Log collection engine) collects Logs and events data, Parse and Transform. Logstash is a tool for managing events and logs. Logstash is a system of log collection, processing, storage and searching activities. Basically, it collects, processes, and forwards events and log messages. The Collection can be completed via configuring the “Input plugins” including raw socket/packet communication, file tailing, and several message bus clients. Once an input plugin has collected data it can be processed by any number of filters which modify and give an explanation of the event data. Finally, logstash will route the event data to output plugins which can forward the events to a variety of external programs including Elasticsearch, local files and several message bus implementations.
A Logstash pipeline has two required elements, input and output, and one optional element, filter. The input plugins consume data from a source, the filter plugins modify the data as you specify, and the output plugins write the data to a destination.
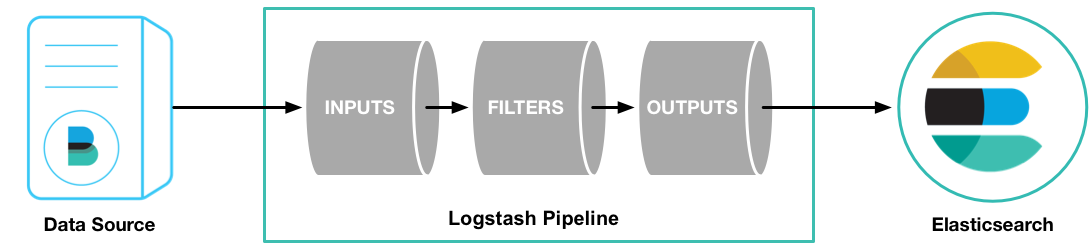
Logstash can collect logs from sources using input plugins, process the data into a common format using filters, and stream data using output plugins. Logstash accepts data from all shapes and size of data. Logstash will move the data and store it into different storage for further analysis. Check the below-given image for further information:

1. For analysis, we can use datastore like MongoDB or elasticsearch
2. For archiving we can store data in the s3/Google storage
3. For monitoring, we can use Nagios/Graphite
Logstash Plug-ins
Logstash has a collection of input, filter and output plugins.
Input Plugins: Enables ‘event’ that can be read by logstash
Filter Plugins: Performs processing of an event
Output Plugins: Sends event data to a different destination
Logstash pipeline: Basic configuration syntax of the logstash pipeline
Input Plugins | Filter Plugins | Output Plugins |
Beats | Aggregate | CSV |
Elasticsearch | CSV | Elasticsearch |
Kafka | Date | |
Graphite | geoip | File |
Heartbeat | grok | Graphite |
Tttp | Json | Http |
JDBC | sleep | Jira |
File | urlencode | Kafka |
Log4j | UUID | Nagios |
Redis | XML | Redis |
Stdin | Stdout | |
TCP | S3 | |
| | TCP | |
UDP |
Logstash configuration file contains the input and output element and the optional element filter. The Input plugin consumes the data from the source and the filter plugin modifies the data as you specify and an output plugin will write the data to the destination.
Configuration Files, Logs, and the Settings Files in the Appropriate Locations for the System
Type | Description | Default Location |
home | Home directory Installation | /usr/share/logstash |
bin | Binary scripts including logstash to start Logstashand logstash -plugin to install plugins | /usr/share/logstash/bin |
settings | Configuration files, JVM.options and startup.options including logstash.yml | /etc/logstash |
conf | Logstash pipeline configuration files | /etc/logstash/conf.d/*.conf |
logs | Log files | /var/log/logstash |
plugins | Local, non-Ruby-Gem plugin files. Each plugin is contained in a subdirectory. Recommended for development only. | /usr/share/logstash/plugins |
data | Data files used by logstash and its plugins for any persistence needs | /var/lib/logstash |
If you require help, contact SupportPRO Server Admin